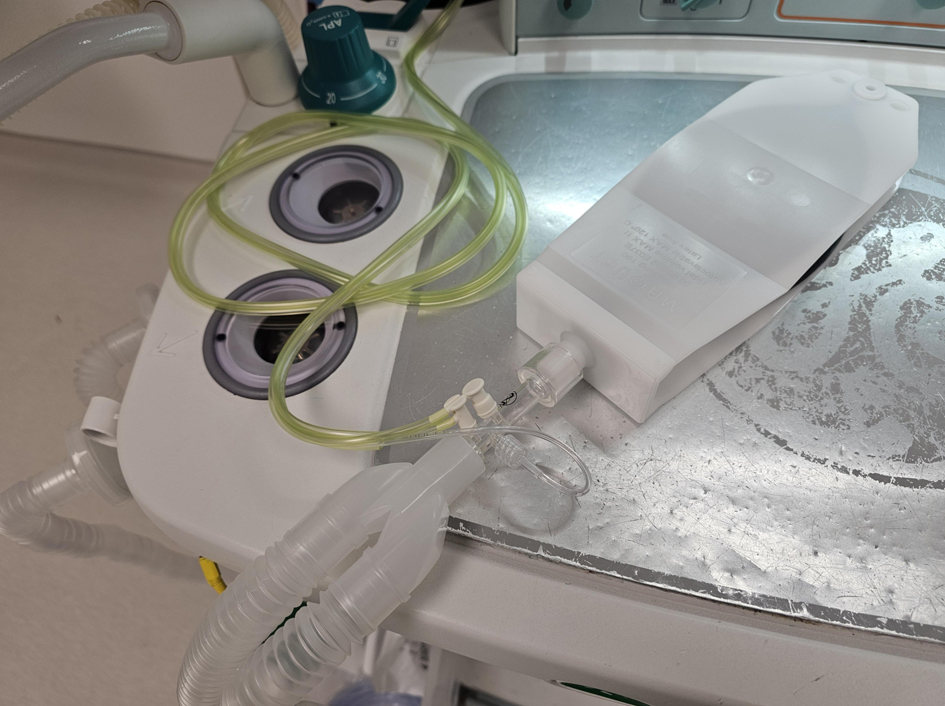
Figure 1. Photograph of the lung analogue device used in the current study. The pneumotachometer is attached between the anesthesia circuit and the 15 mm attachment to the lung analogue device.
| International Journal of Clinical Pediatrics, ISSN 1927-1255 print, 1927-1263 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Int J Clin Pediatr and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.theijcp.org |
Original Article
Volume 13, Number 3, December 2024, pages 69-72
Accuracy of the Set Tidal Volume During Intraoperative Anesthetic Care: An In Vitro Evaluation
Figure

Tables
| Setting | Patient mode | Ventilator mode |
|---|---|---|
| The data are presented as the mean ± SD. Each value was calculated from 250 breaths. The volumes listed as patient mode were measured by the pneumotachometer placed between the 15 mm adaptor of the endotracheal tube and the ventilator circuit. The volumes listed as ventilator mode were measured internally by the anesthesia machine. SD: standard deviation; PIP: peak inflating pressure; Vt: tidal volume. | ||
| Vt 50 mL | 51 ± 0.2 | 50 ± 0.1 |
| Vt 100 mL | 97 ± 0.2 | 100 ± 0.2 |
| Vt 200 mL | 190 ± 0.2 | 200 ± 0.7 |
| Vt 300 mL | 285 ± 0.2 | 300 ± 0.1 |
| PIP 15 cm H2O | 164 ± 0.9 | 173 ± 0.5 |
| PIP 20 cm H2O | 258 ± 0.1 | 274 ± 0.5 |
| Setting | Patient mode | Ventilator mode |
|---|---|---|
| The data are presented as the mean ± SD. Each value was calculated from 250 breaths. The volumes listed as patient mode were measured by the pneumotachometer placed between the 15 mm adaptor of the endotracheal tube and the ventilator circuit. The volumes listed as ventilator mode were measured internally by the anesthesia machine. SD: standard deviation; PIP: peak inflating pressure; Vt: tidal volume. | ||
| Vt 50 mL | 52 ± 0.6 | 52 ± 0.4 |
| Vt 100 mL | 100 ± 0.5 | 101 ± 0.4 |
| Vt 200 mL | 202 ± 0.5 | 200 ± 0.4 |
| Vt 300 mL | 305 ± 0.6 | 302 ± 0.5 |
| PIP 15 cm H2O | 174 ± 0.8 | 172 ± 0.6 |
| PIP 20 cm H2O | 277 ± 0.6 | 274 ± 0.6 |