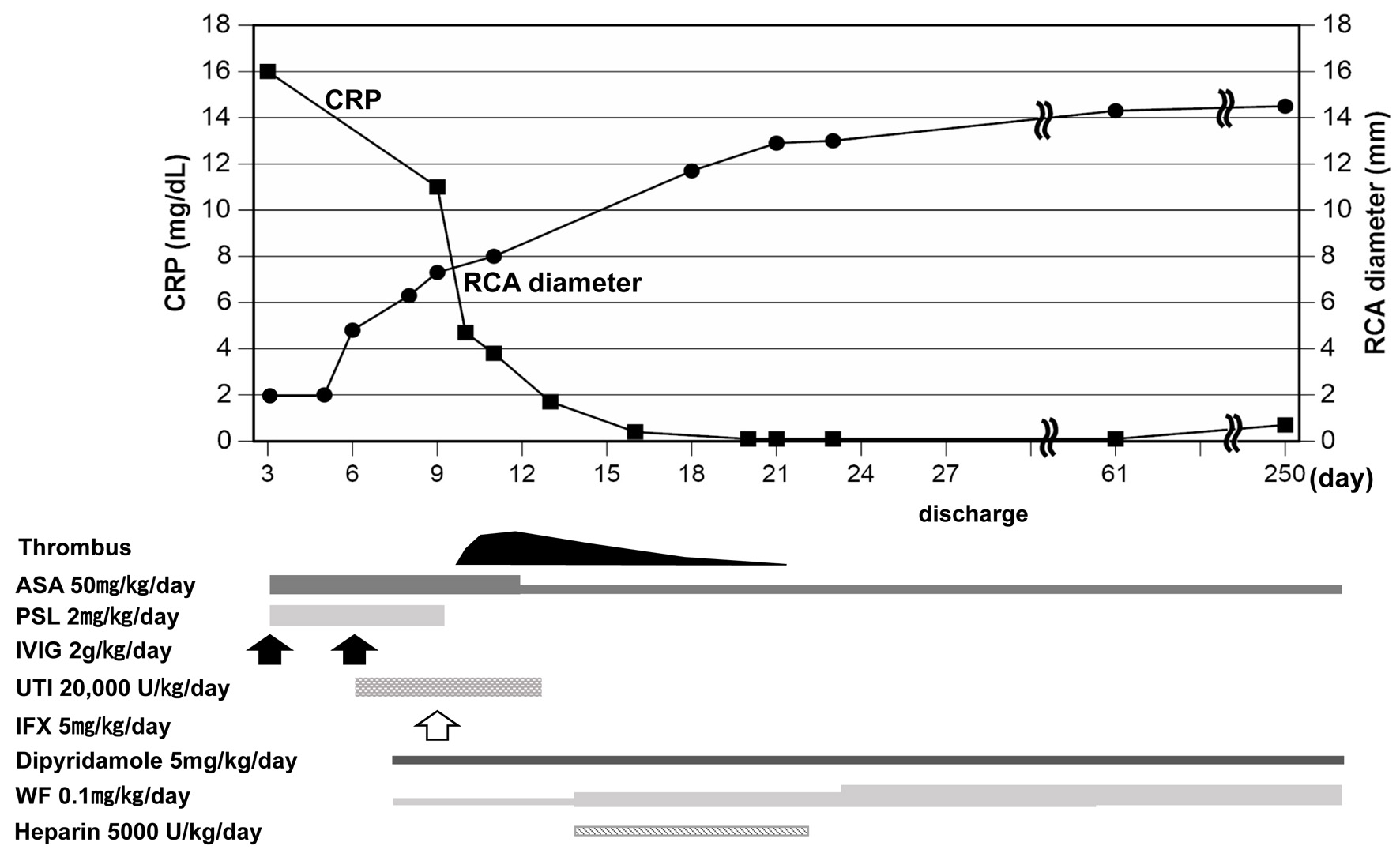
Figure 1. Clinical course after admission. Upper panel shows changes in RCA diameter and CRP levels and lower panel shows time course of applied medicine. ASA: aspirin; PSL: prednisolone; IVIG: intravenous immunoglobulin; UTI: ulinastatin; IFX: infliximab; WF: warfarin; RCA: right coronary artery; CRP: C-reactive protein.
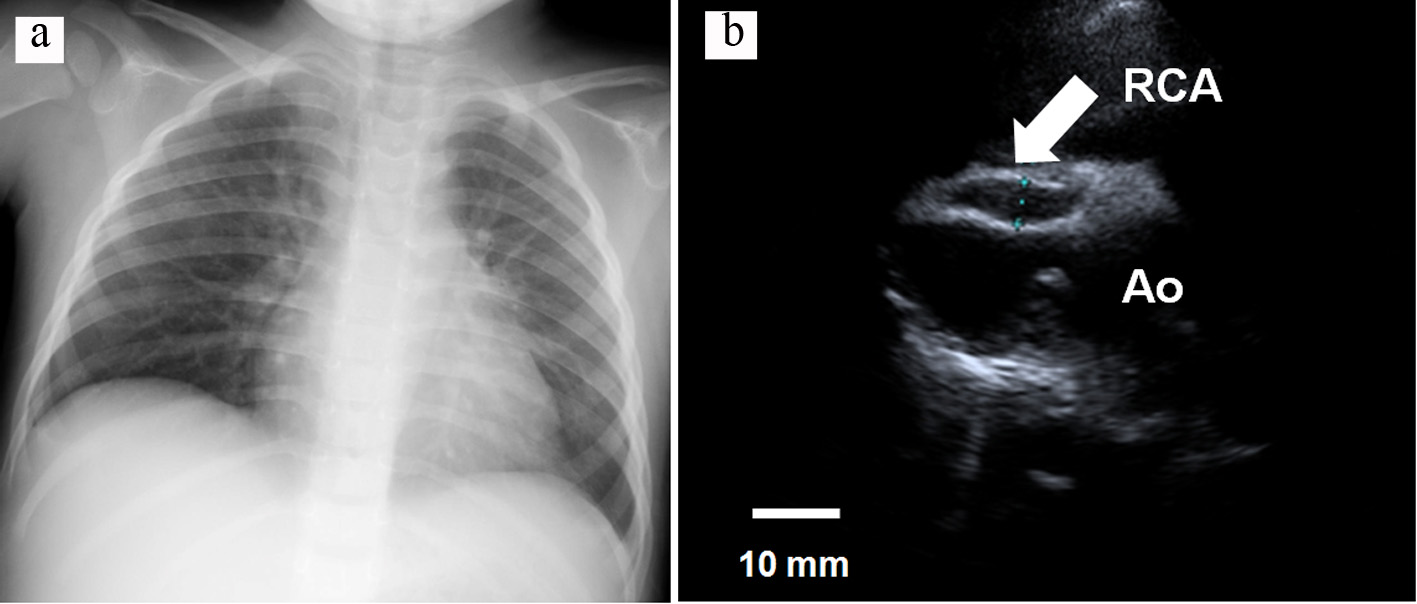
Figure 2. (a) Chest X-ray showing the CTR was 50% without cardiomegaly, and (b) transthoracic echocardiogram, showing the RCA was 7.3 mm in diameter and a thrombus was not detected inside the aneurysm. RCA: right coronary artery; Ao: ascending aorta; CTR: cardiothoracic ratio.
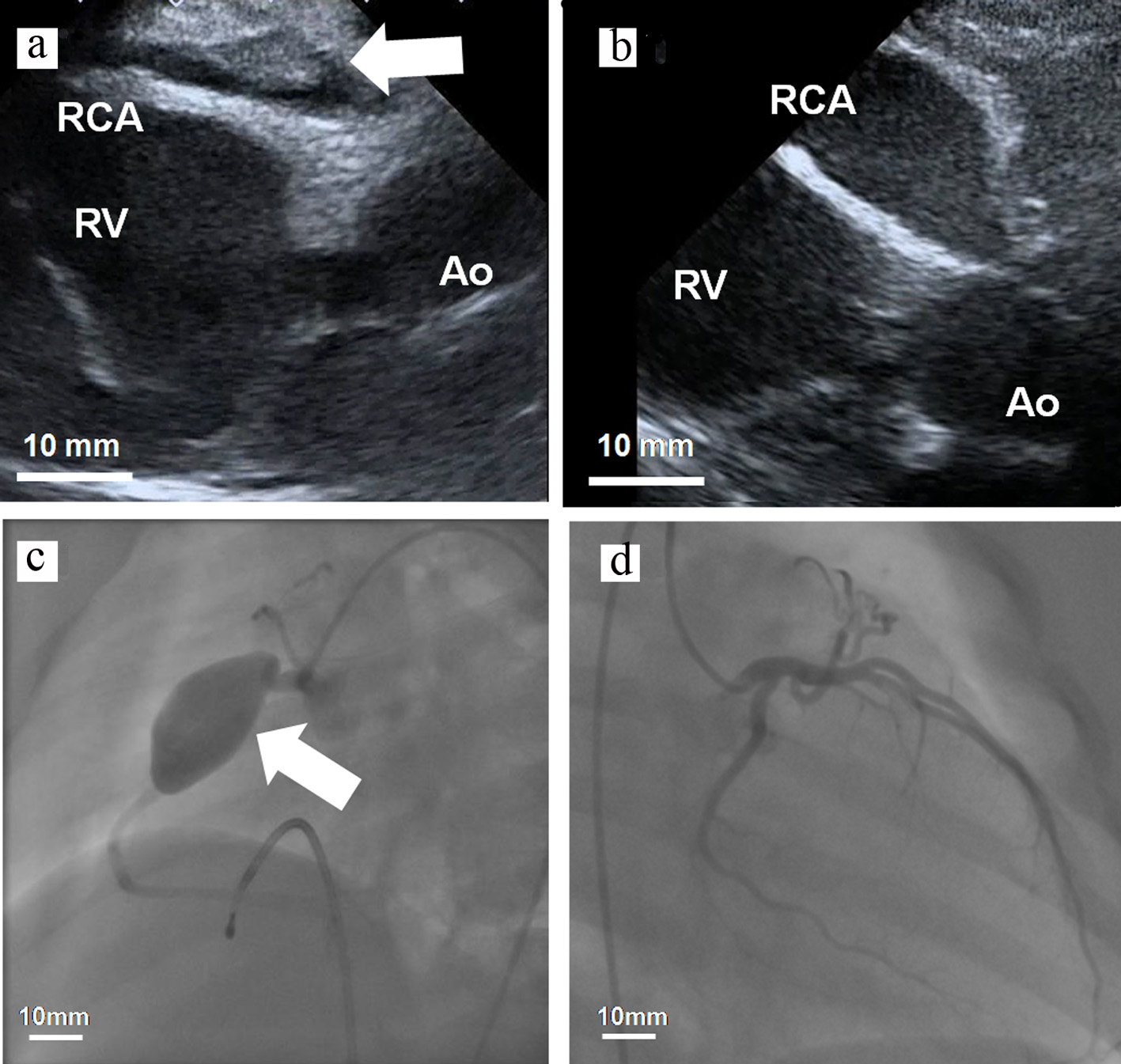
Figure 3. (a, b) Transthoracic echocardiogram and (c, d) coronary angiogram. (a) The RCA was 7.3 mm in diameter and a thrombus (4.5 × 15.7 mm) was detected inside the aneurysm (day 10). (b) The size of the RCA was 14.3 × 31.4 mm in diameter without a thrombus (day 61). RCA: right coronary artery; Ao: ascending aorta; RV: right ventricle.


