Figures
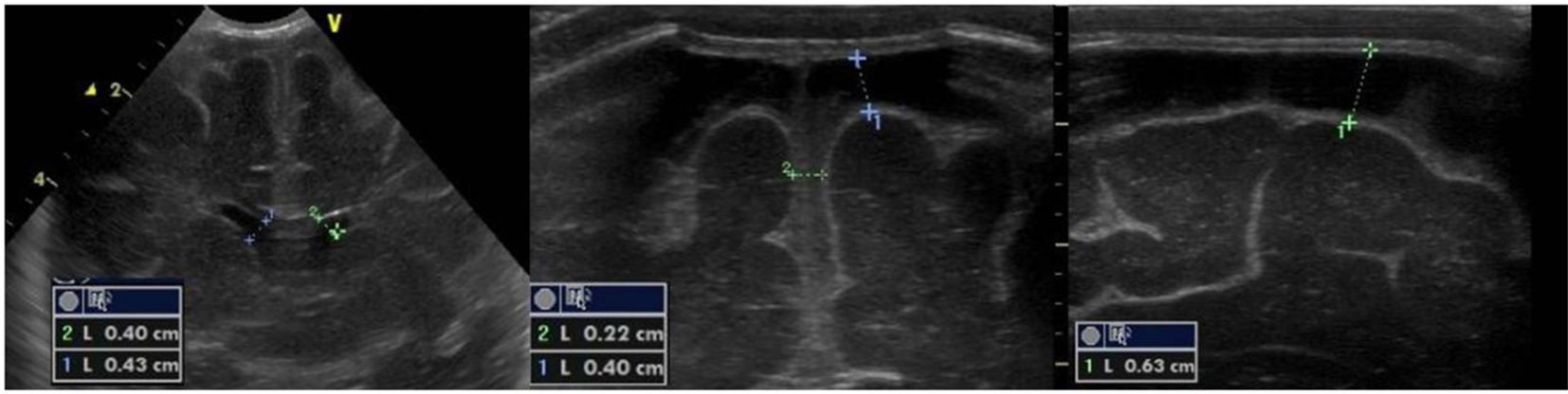
Figure 1. Echogenic widening of brain’s sulci and interhemispheric fissure associated with meningeal thickening; mild ventricular enlargement.
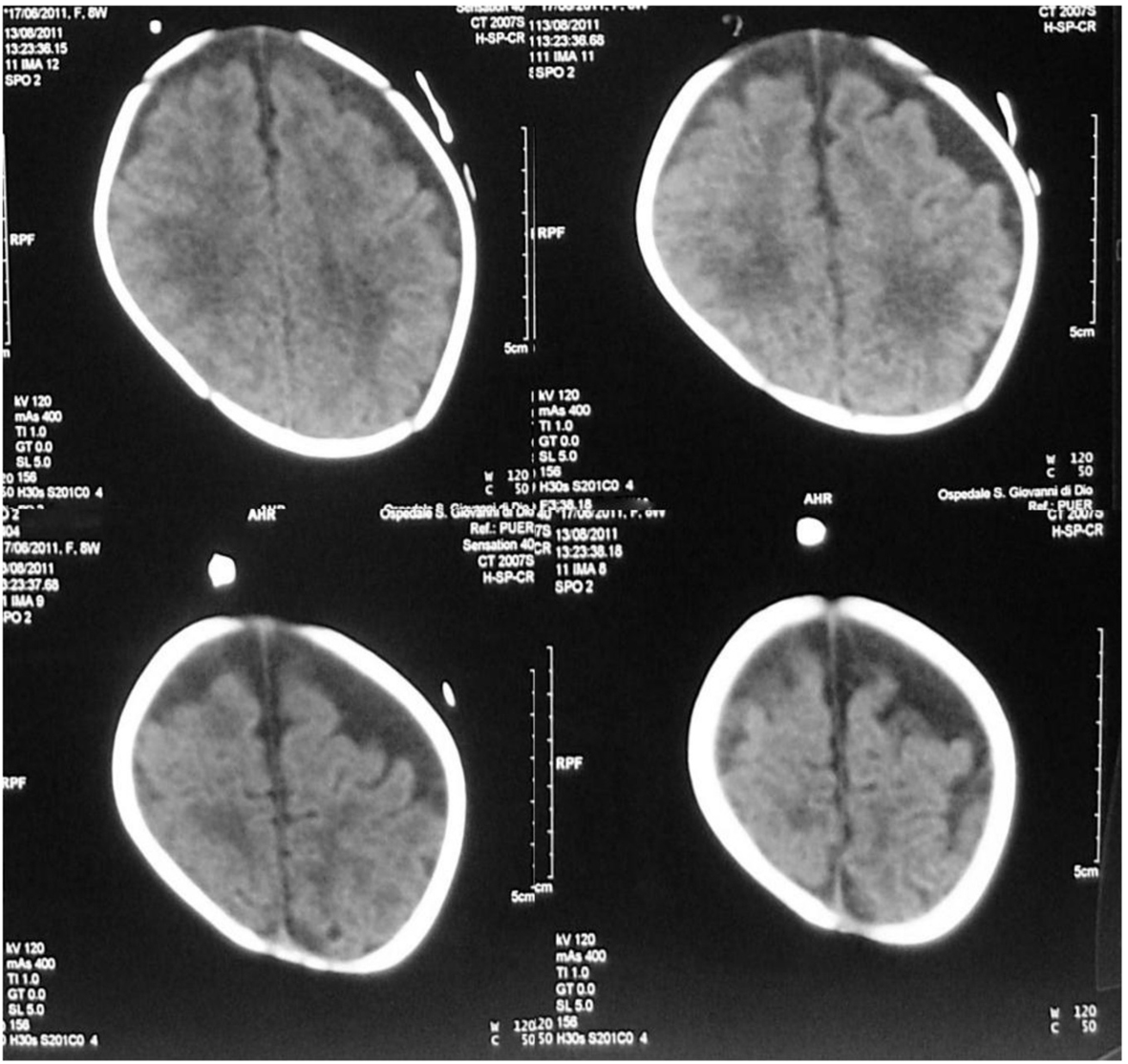
Figure 2. Brain MRI: bilateral asymmetrical subdural effusions, prevalent on the right side of the brain.
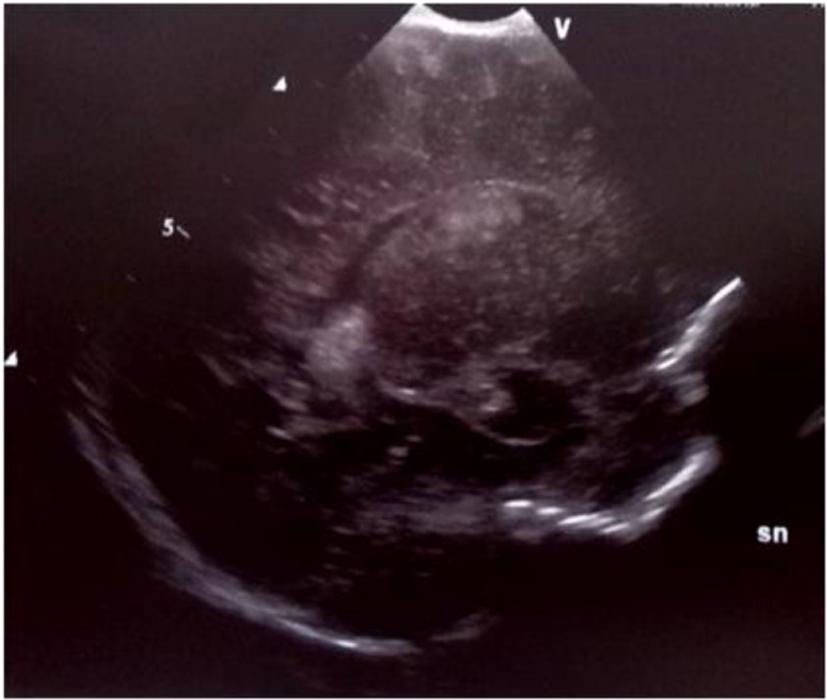
Figure 3. Parasagittal section: multiple echodensities of the left caudate.
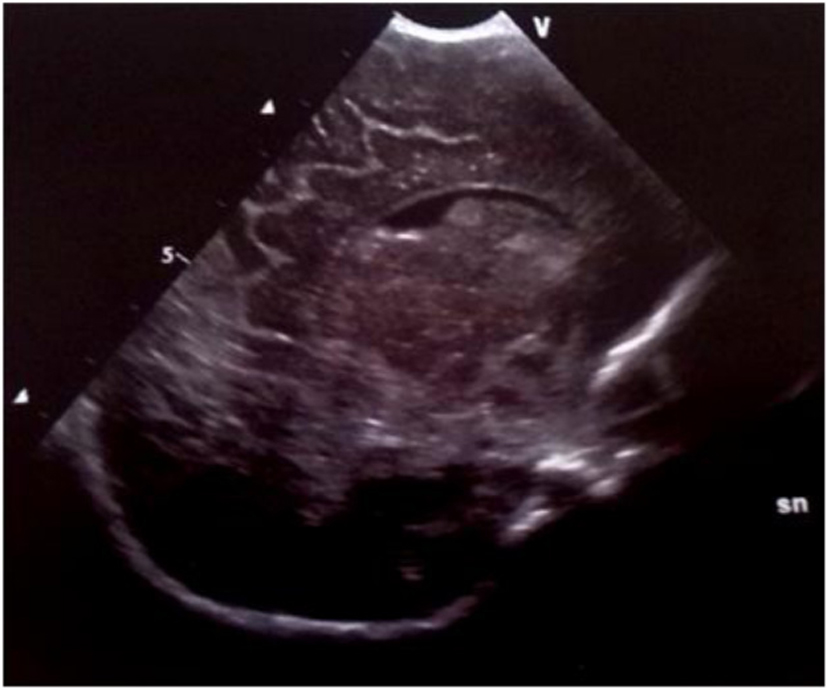
Figure 4. Parasagittal section: multiple echodensities of the caudate head.
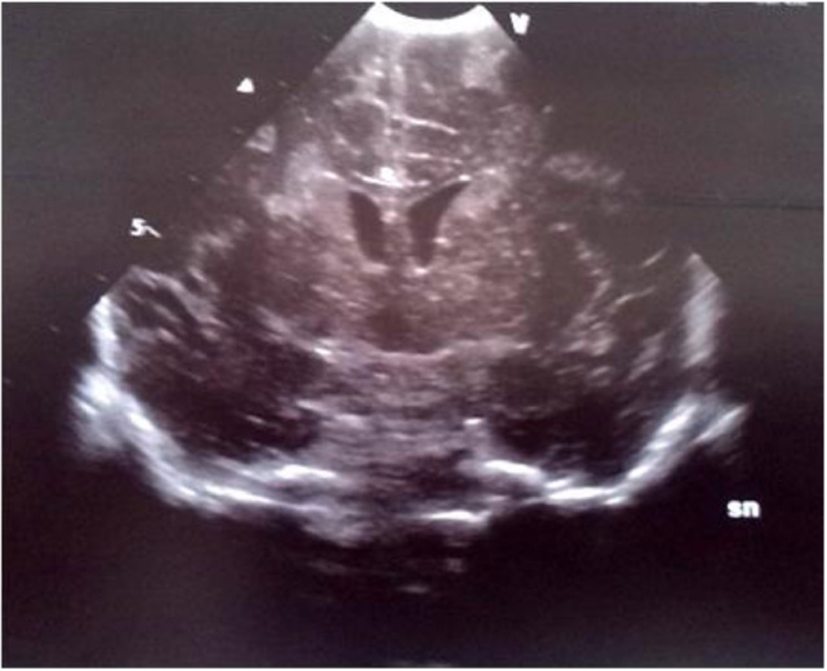
Figure 5. Coronal section: bilateral echodensities of the caudate and of the right periventricular white matter.
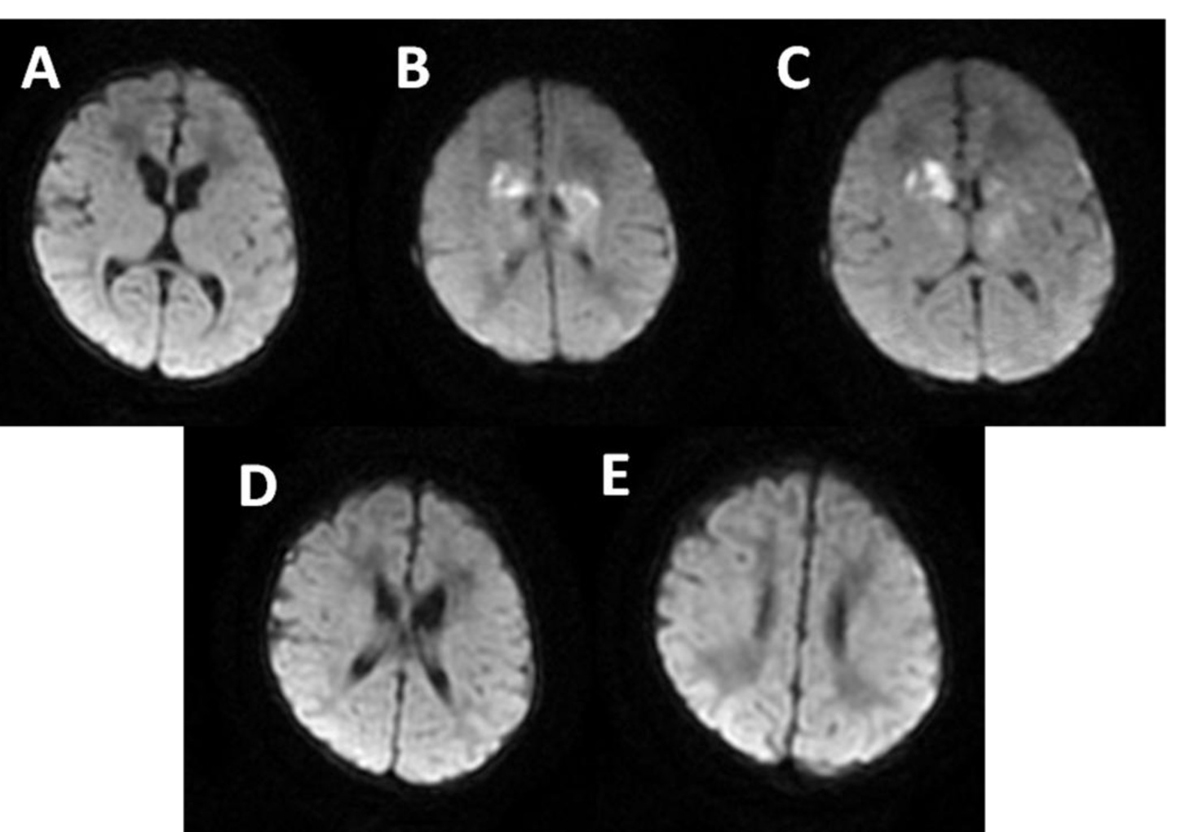
Figure 6. MRI: multiple and confluent ischemic areas (B-C) in the basal ganglia and frontal periventricular white matter.
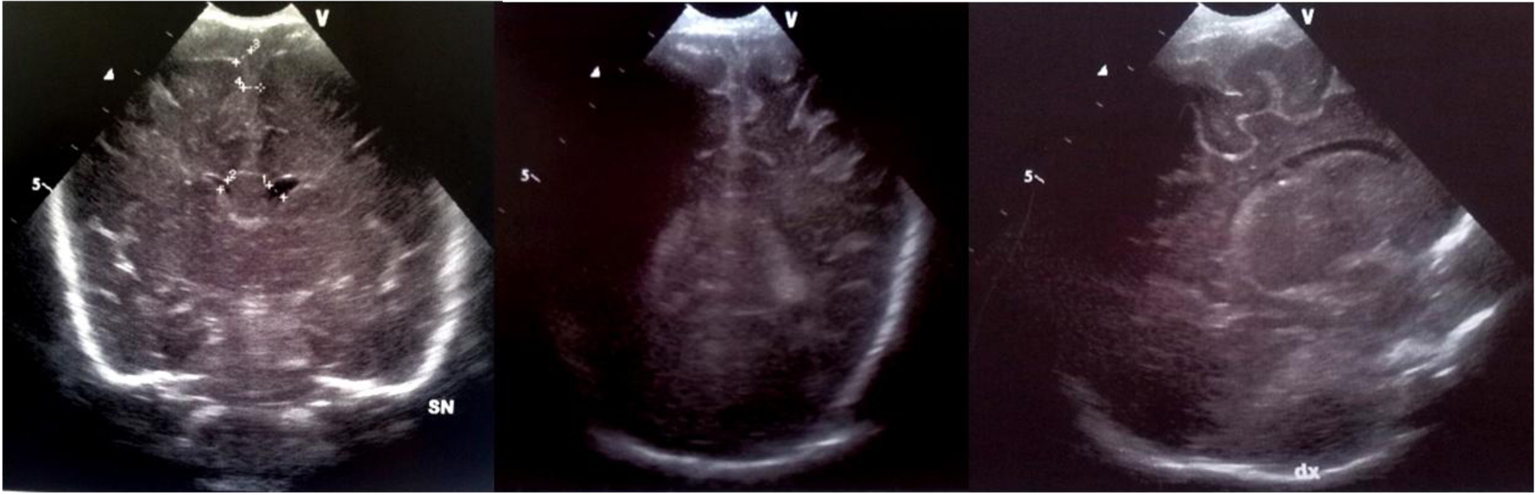
Figure 7. Echogenic widening of brain sulci and interemispheric fissure.
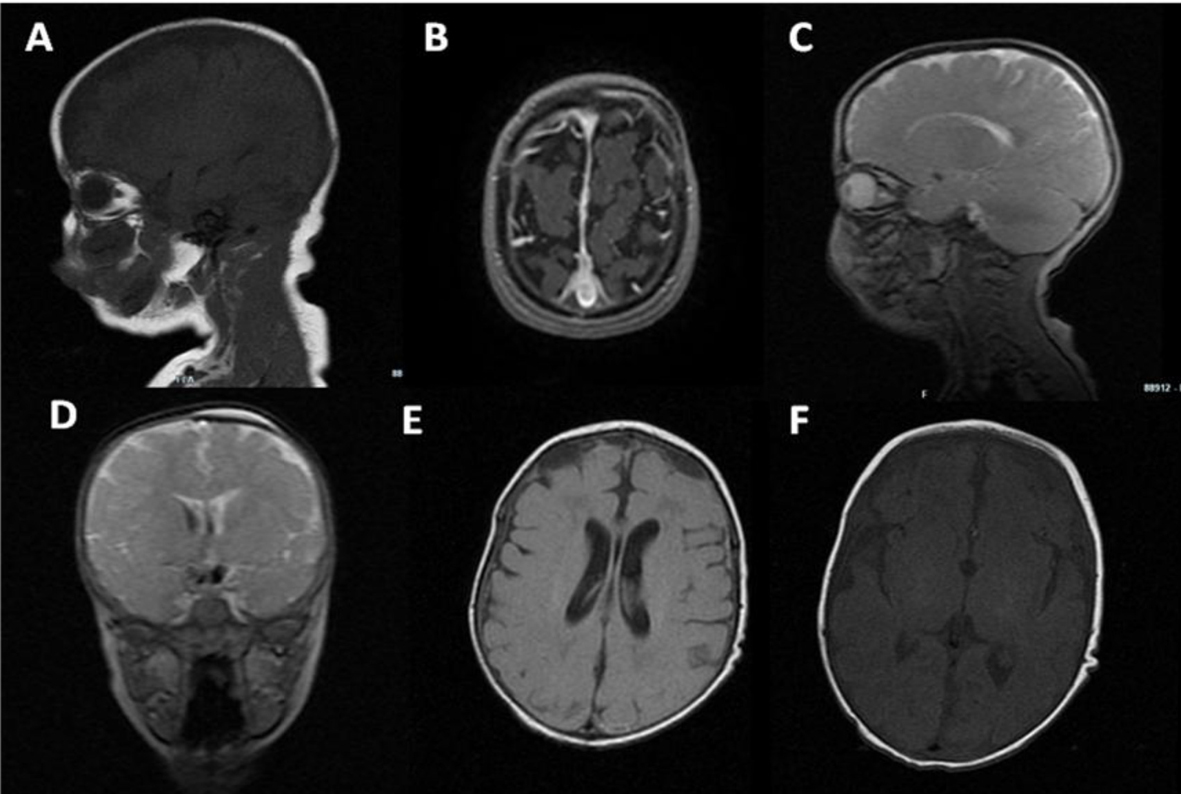
Figure 8. MRI: biconvex subdural effusions (A-E); strand formation within the lateral ventricles (D-E); ischemic foci in the basal ganglia (C, F); bilateral frontal periventricular ischemic areas (E).
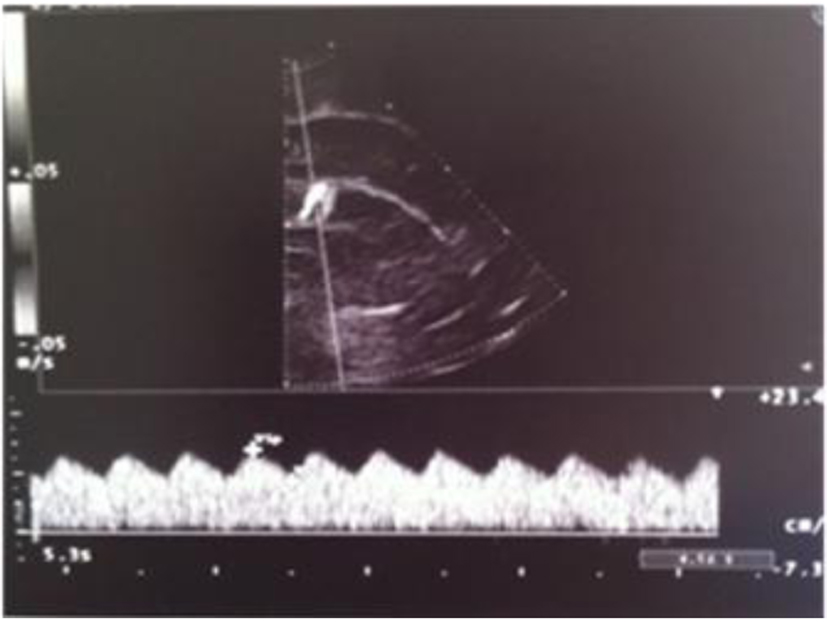
Figure 9. Abnormal resistance index (RI = 0.35).
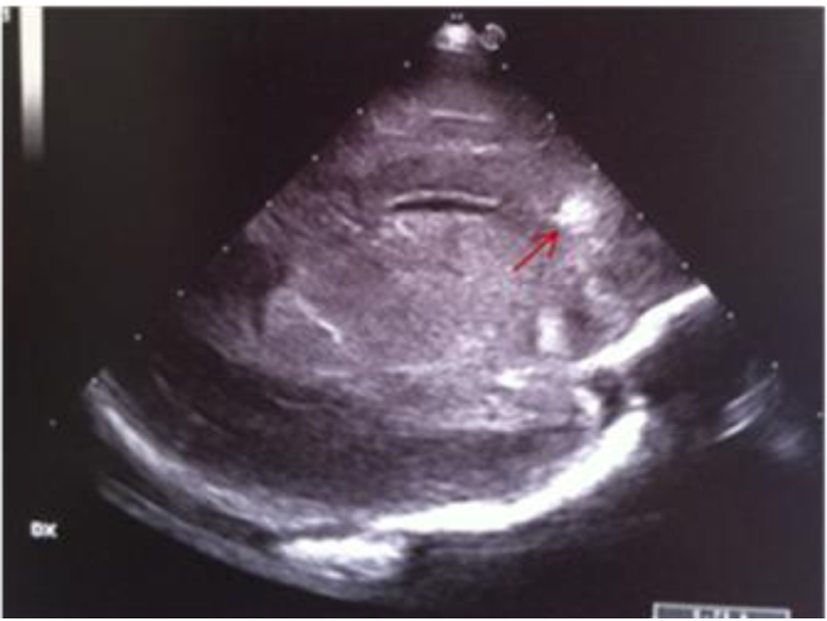
Figure 10. Parasagittal section: frontal periventricular echodensity (red arrow).
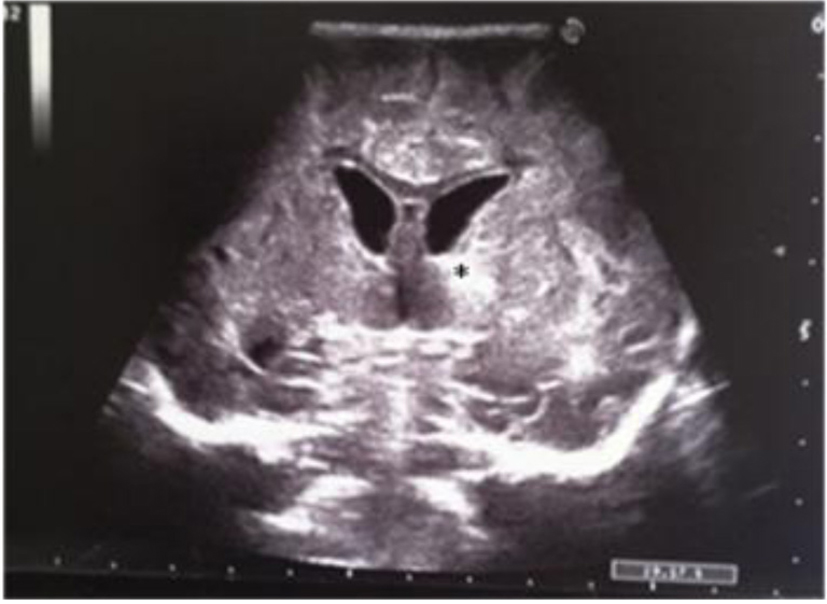
Figure 11. Coronal section: asymmetric widening of lateral ventricles; single and localized echodensity in the left thalamus (black star).
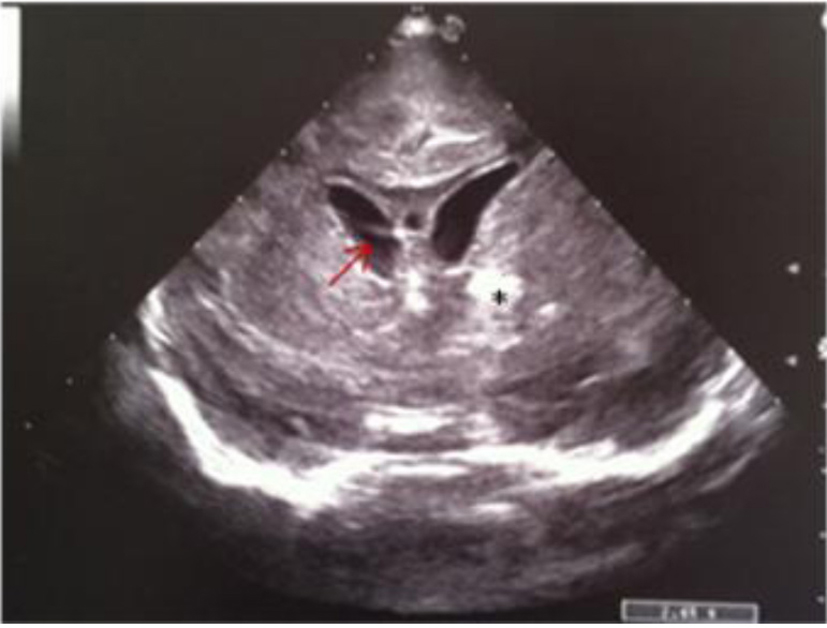
Figure 12. Coronal section: asymmetric widening of lateral ventricles; intraventricular strand (red arrow); localized echodensity in the left thalamus (black star).
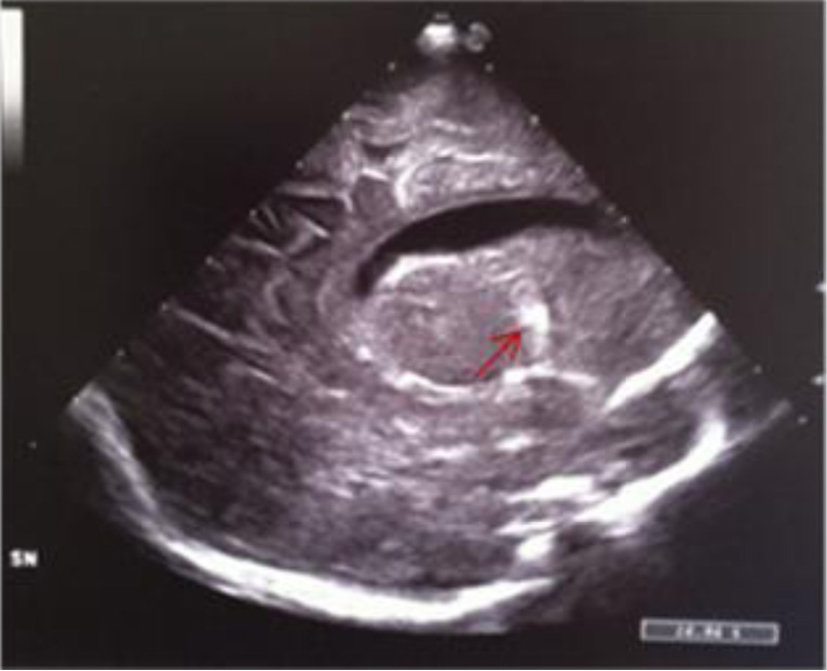
Figure 13. Median parasagittal section: widening of the left lateral ventricle and localized echodensity in the left thalamus (red arrow).
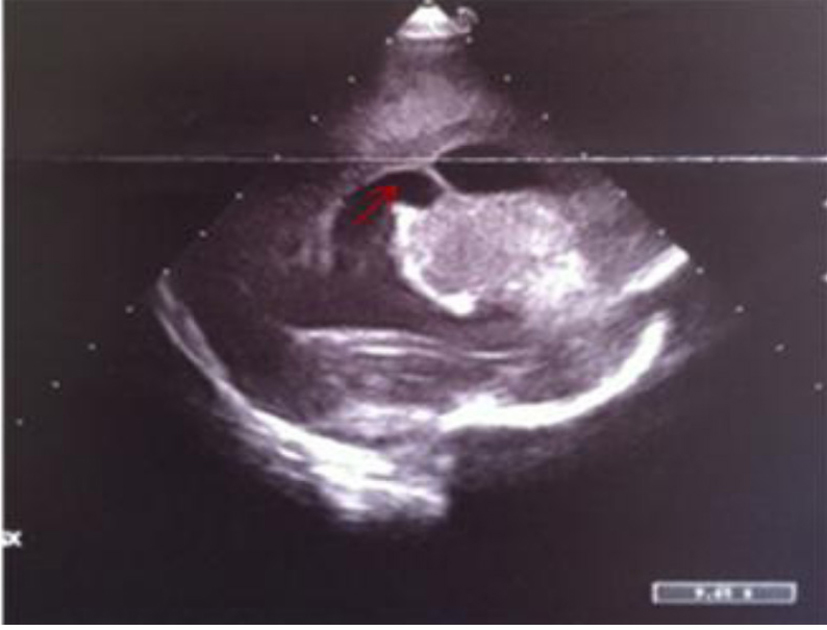
Figure 14. Left parasagittal image: widening of lateral ventricle with a septum inside (red arrow) and localized echodensities of anterior thalamus.
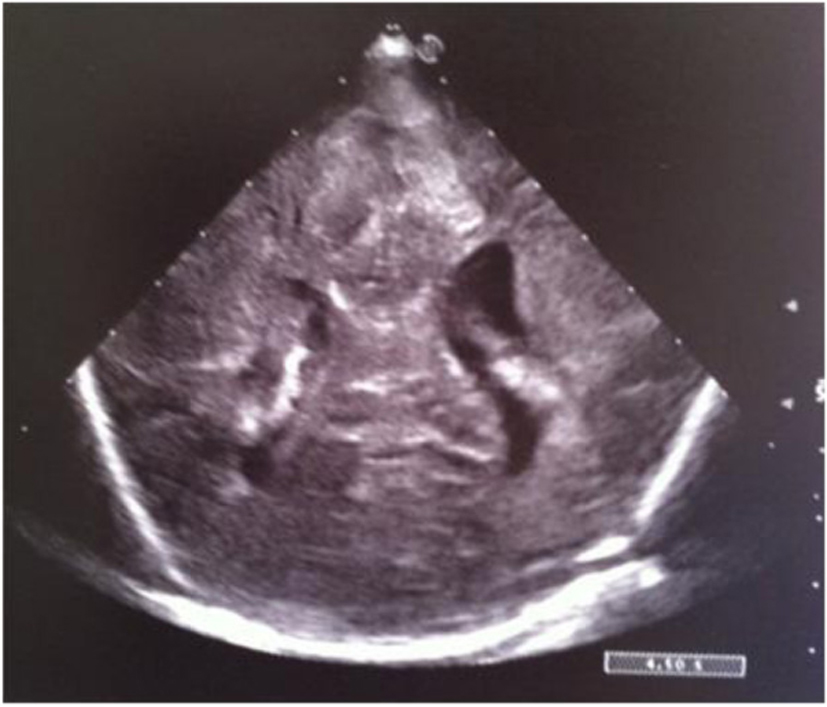
Figure 15. Coronal section: asymmetric widening of lateral ventricles.
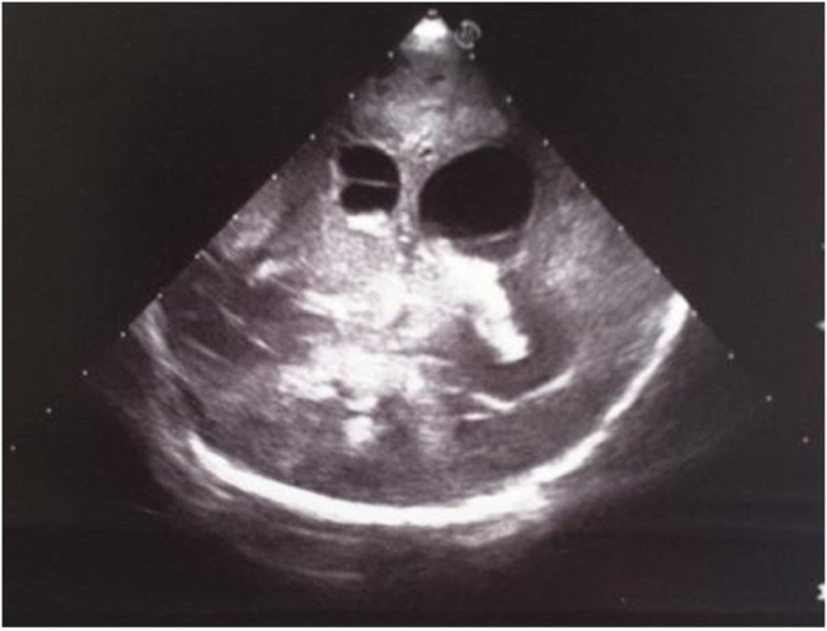
Figure 16. Coronal section: asymmetric widening of lateral ventricles; intraventricular strand; localized echodensity in the left thalamus.
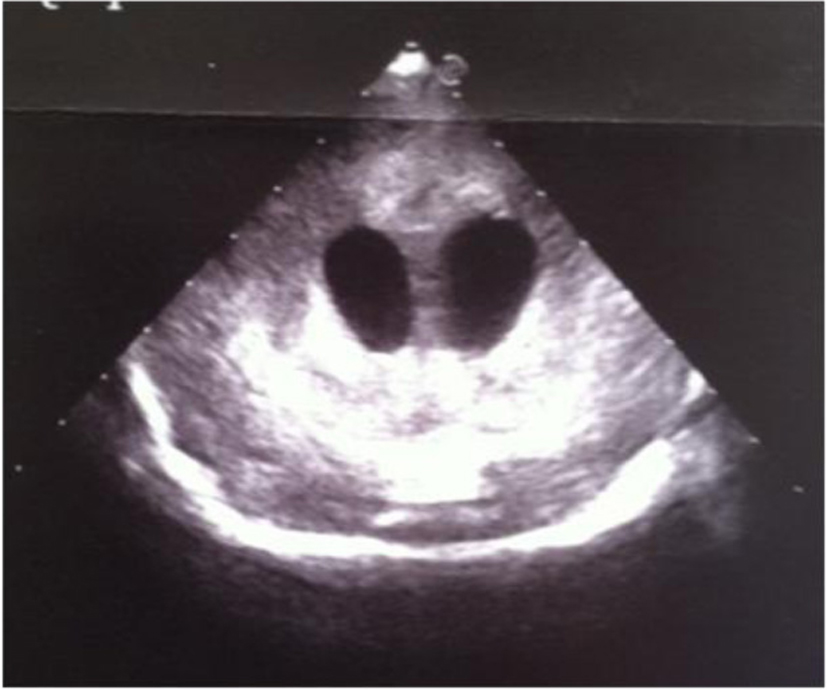
Figure 17. Coronal section: widening of the lateral ventricles and hyperechoic basal ganglia.
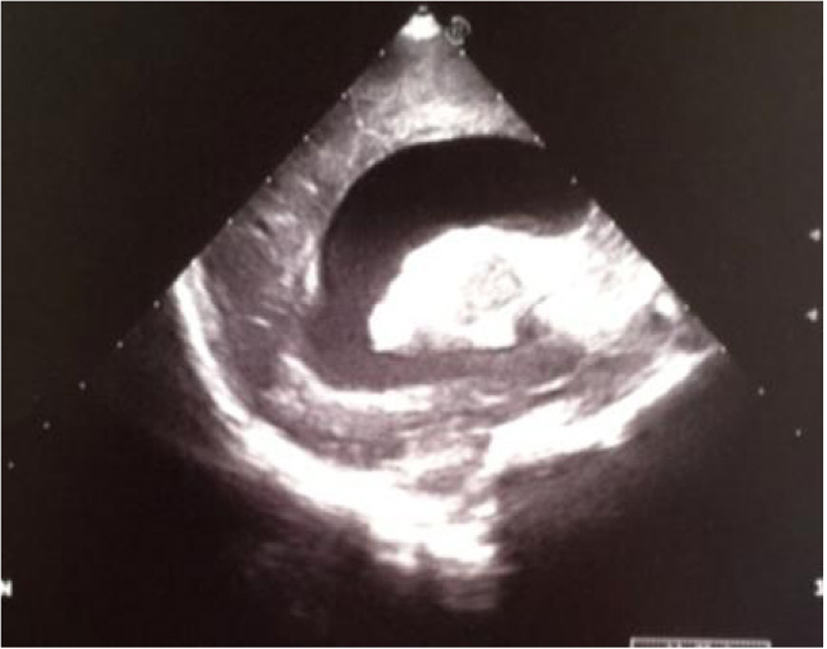
Figure 18. Sagittal section: severe widening of the left lateral ventricle and hyperechoic basal ganglia.
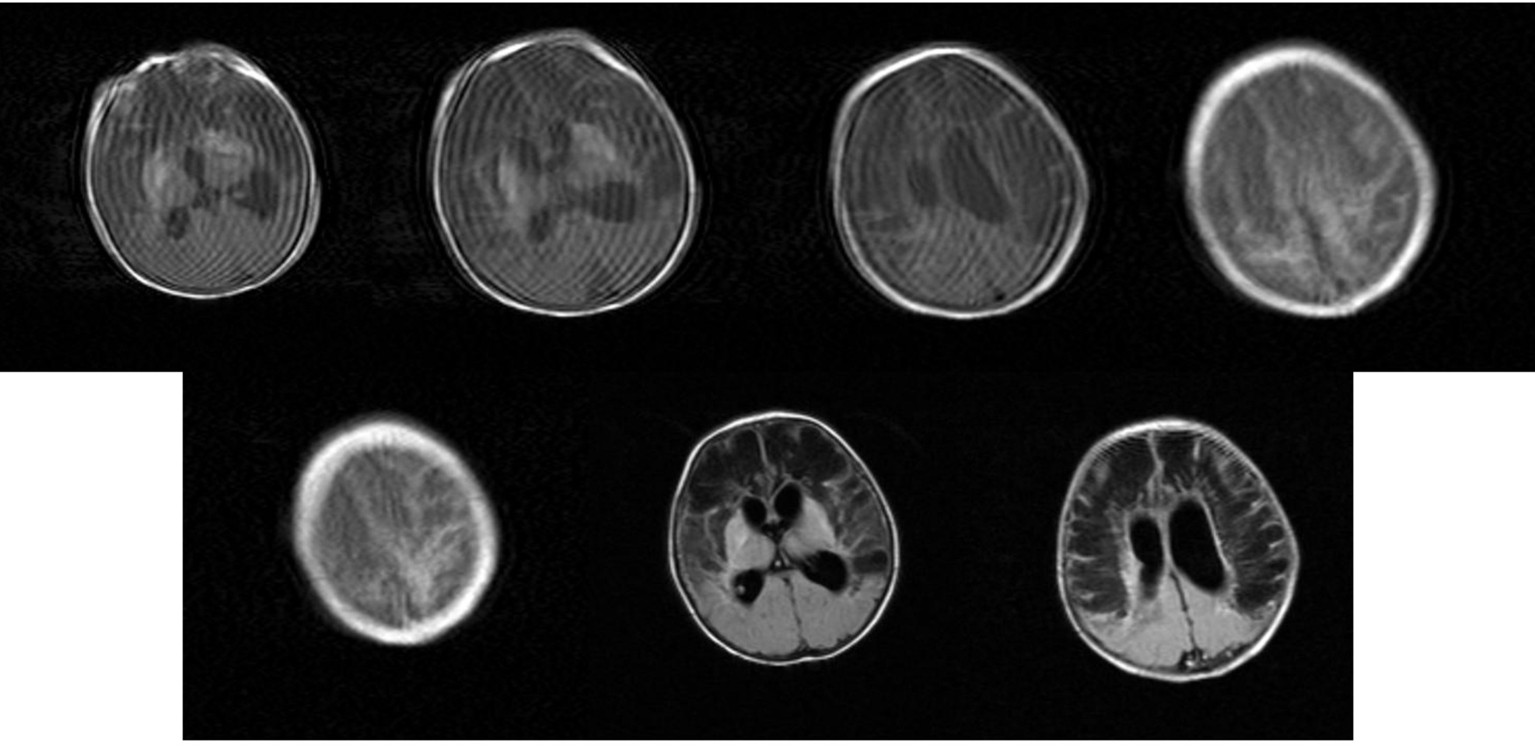
Figure 19. MRI: Movement artfacts. Bilateral multiple extensive cysts in the fronto-parietal white matter and focal bilateral emorrhages of lenticular nucleus. Obstructive triventricular hydrocephalus.
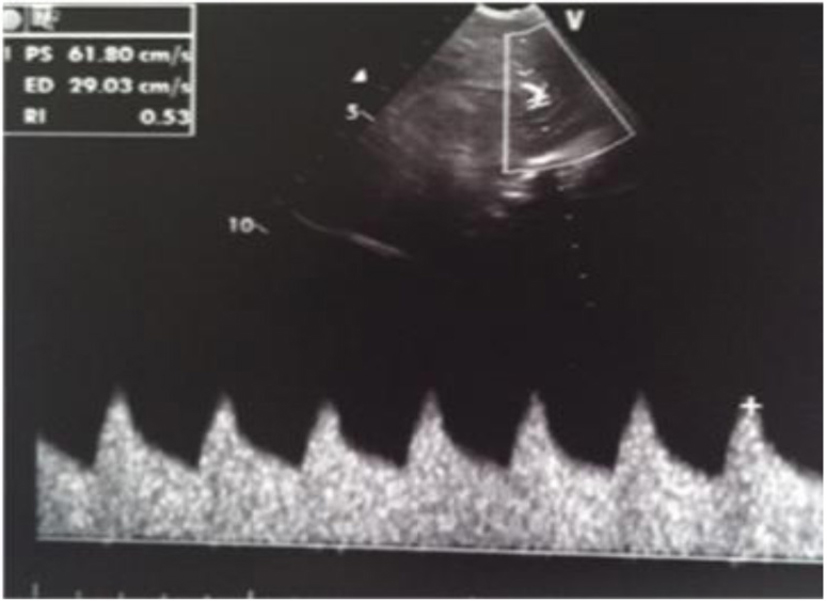
Figure 20. Normal resistance index (IR) but evidence of increased telediastolic velocity.
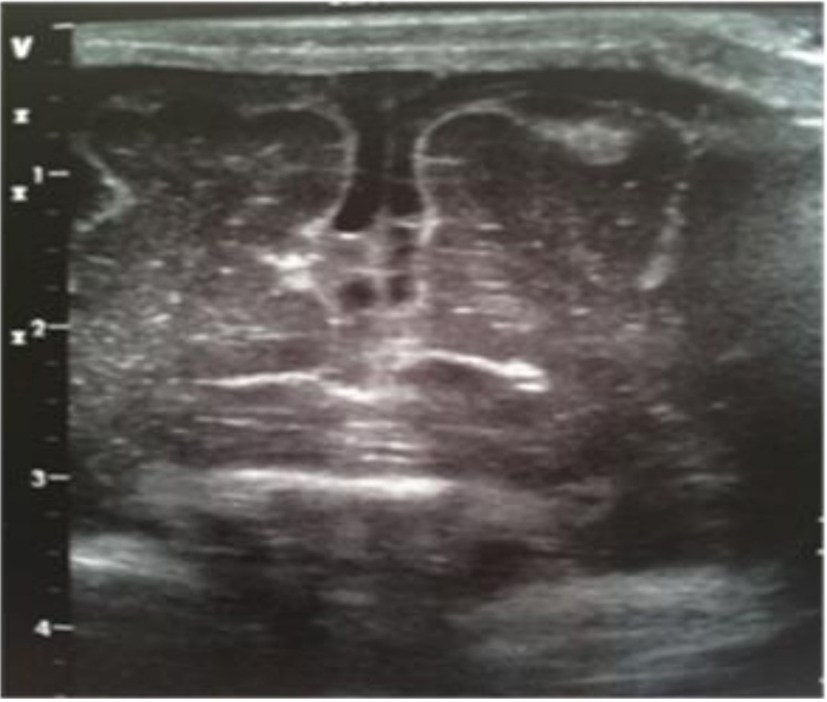
Figure 21. Coronal section: mild widening of interhemispheric fissure with subarachnoid echogenic strands.
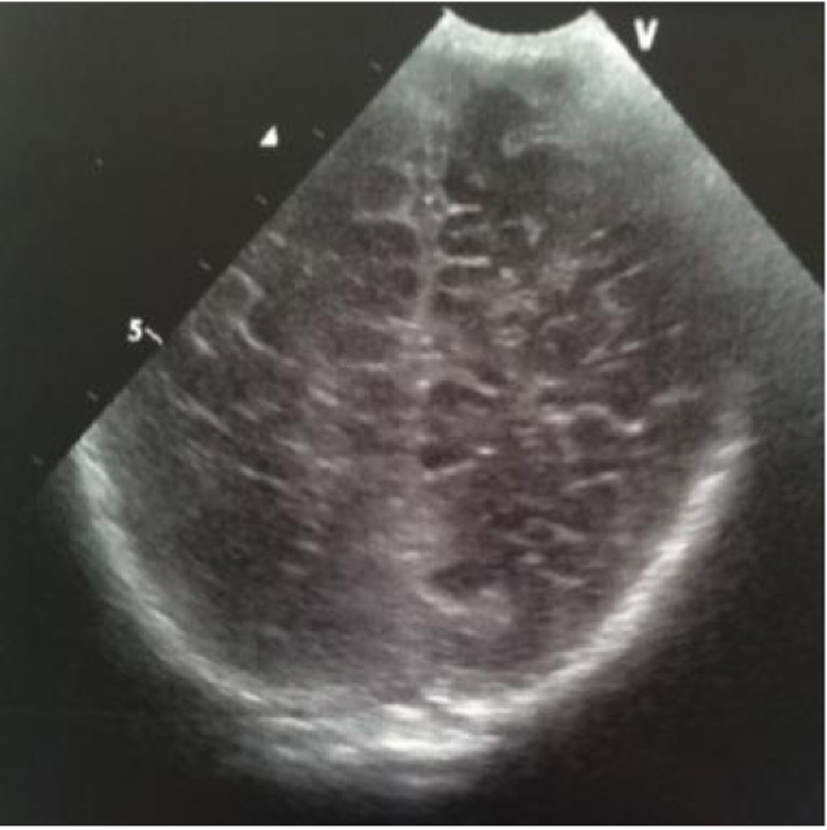
Figure 22. Coronal section: echogenic widening of posterior interhemispheric fissure.
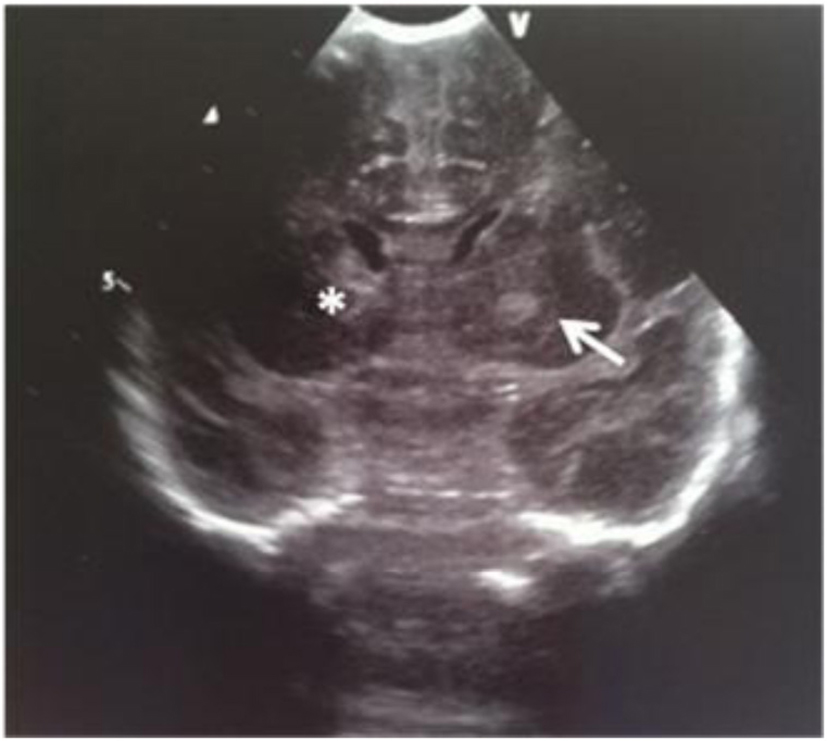
Figure 23. Coronal section: asymmetric lateral ventricles; rounded echodensity in the left thalamus (arrow) and incipient cavitation of both left caudate nucleus and thalamus (star).
Table
Table 1. Summary of Six Cases of GBS Meningitis
| Patients | EG (weeks)/PN (g) | Sex/age | Clinical findings | US | MR/CT | Outcome |
|---|
| 1 | 32/1,450 | F/2 months | Septic status, fever, high-pitched cry, bregmatic fontanel bulging, nuchal rigidity, SIADH | Diffuse thickening of the leptomeninges | Frontal bilateral subdural effusions | Collections drainage; no global delay at 3 years of age |
| 2 | 39/3,360 | F/4 days | Feeding intolerance, fever, seizure, hypotonia | Edema, hydrocephalus, bilateral frontal cysts | Ventriculitis; bilateral basal ganglia and frontal ischemic lesions evolving in cysts | No global delay at 1 and 3 months of age |
| 3 | 32/2,150 | F/38 days | Fever | Bilateral subdural empyema | Bilateral subdural empyema, dural thrombosis of the left transversal sinus | Empyema drainage; no global delay at 3 years of age |
| 4 | 38/2,280 | F/3 days | Fever, feeding intolerance | Edema, obstructive triventricular hydrocephalus, bilateral frontal cysts | Frontal and parietal white matter cysts, abnormal signal of frontal, parietal and deep gray matter (putamen and pallidus) | Increased muscle tone at 50 days of age |
| 5 | 39/3,190 | M/1 day | Fever, pale cianosis, hyperreactivity | Bilateral hyperecoic basal ganglia, interhemispheric fissure and subarachnoid space | Transversal sinus thrombosis, small cortical hemorrhages with basal ganglia involvement; ischemis of frontal subcortical white matter bilaterally | Mild motor delay; convergent strabismus at 19 months of age |
| 6 | 39/3,070 | F/30 days | Fever, feeding intolerance | Hyperechoic sulci | Not performed | Exitus |























